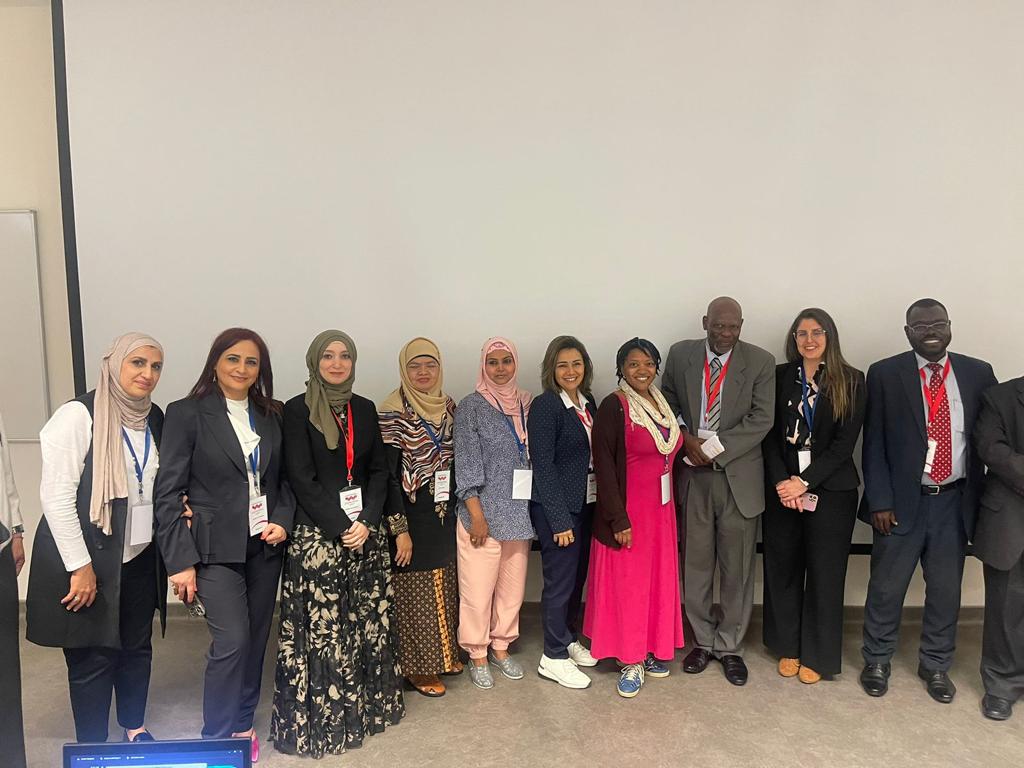
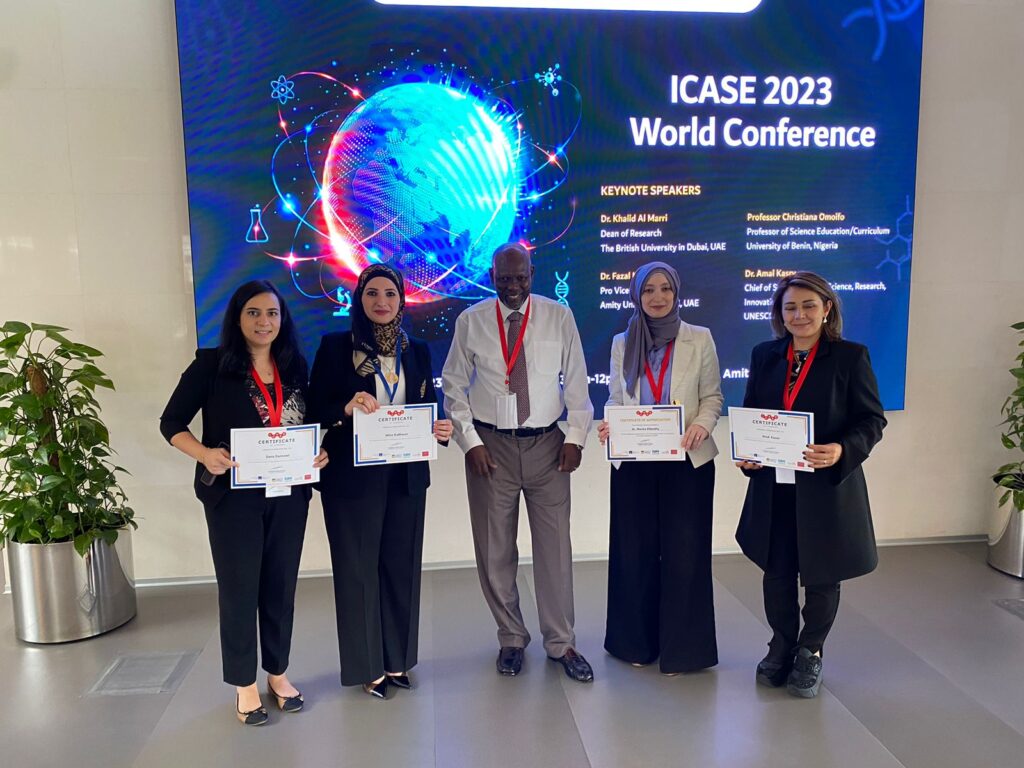
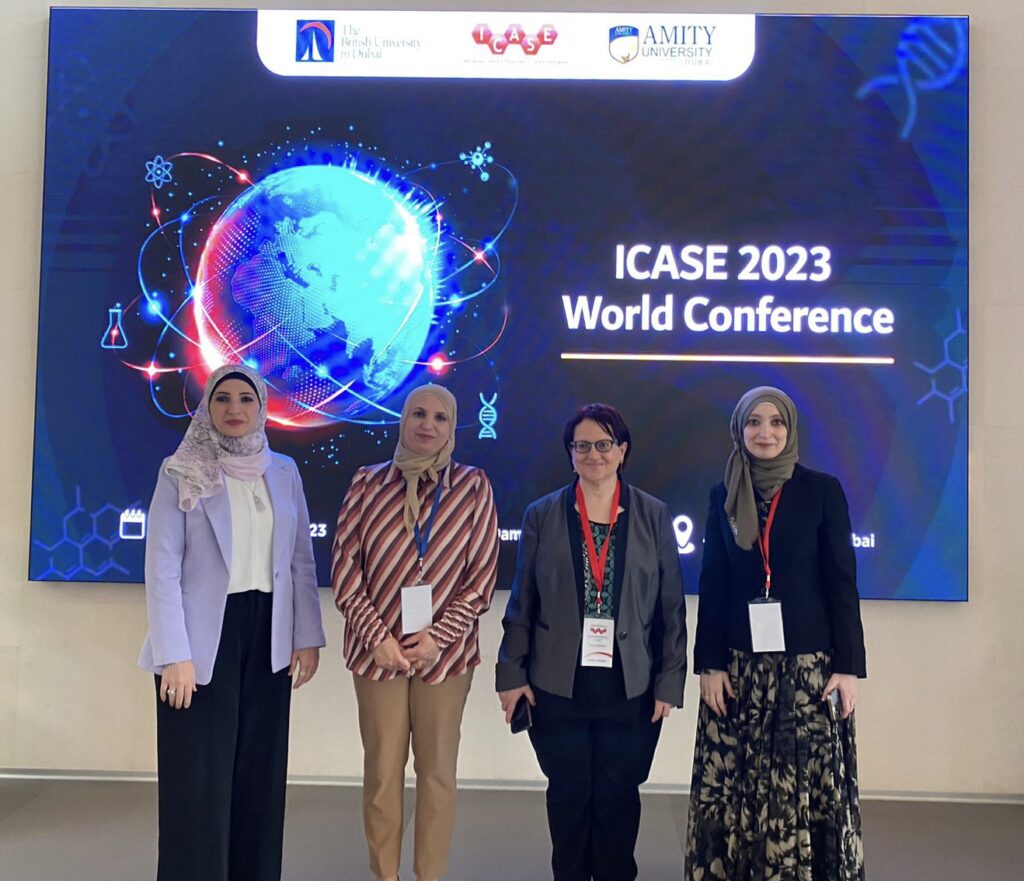
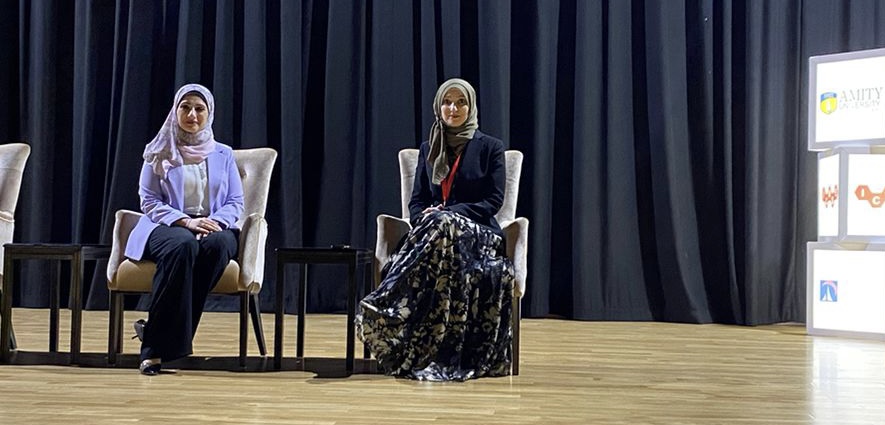
In the International Council of Association for Science Education (ICASE) that was held in Dubai 27 – 30th March 2023 by both The British University in Dubai (BUID), and Amity University, I participated in many different ways:
- A member of the main discussion panel about teaching and learning science
- Session chair who was organizing and leading the discussion of the presentations
- Presenting about Inquiry-based Learning and Standardized exams
Abstract:
My presentation was about how features of inquiry-based learning are highly linked to the assessment criteria of science used in standardized exams like TIMSS. Strategies of inquiry-based learning provides students with authentic learning opportunities that enable students to construct new knowledge, maintain positive attitude towards learning science, and develop new scientifc skills like problem solving, critical thinking and making reasonable decisions that all are measured by TIMSS exams. If we want the the implementation of IBL practices to positively enhance students’ results of standardized exams, we should consider some important factors like the constructive alignment of learning components, apply high level of inquiry practices, and teachers’ beliefs. Strong alignment should be developed between the intended curriculum including the learning objectives, teaching and learning practices that are competency-based, and the assessment criteria of standardized exams that all focus on the acquisition of scientific skills. There are six main categories (cononical knowledge, experimental knowledge, nature of science, real-life issues, metacognitive knowledge, safety of science environment) knowledge that all are connected to the strategic cycle of inquiry model. The question is: which type of inquiry teachers should apply? The continum of inquiry learning starts from structured inquiry where all the learning responsibilities are given to the teachers, while students cat as passive learners only. Going higher in the inquiry continum, Half of the responisbility will be given to students. Foe example: teachers will pose the inquiry questions and conduct the investigation, while students will analyze the data and make a conclusion. Moving forward in the continum will take us to Guided inquiry and then Open inquiry where students are active learners who are taking ownership of their learning and act independently which is highly recommended to enhance students’ competencies. Teachers’ belefs affect their practices. If they belief in the value and importance of IBL, they will focus on the highest levels of inquiry activities to support the learning process.